Problem: Medical Emergencies
Scope: Personal
Impact: Minor, Major (Depending on severity)
Dangers (not limited to): Personal Injury, Death
Preps (not limited to): Learn and Train on Life Saving techniques, Carry a First-Aid kit, Know the allergies, medications, and medical history, of your loved ones.
Medical emergencies can happen unexpectedly and can be scary for both the patient and the caregiver. Knowing how to respond to different types of medical emergencies can help you provide the best possible care and potentially save a life. In this article, we’ll discuss the different types of medical emergencies and how to prepare for them.
Heart Attack:
A heart attack occurs when the blood flow to the heart is blocked, which can cause serious damage to the heart muscle. Symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain, shortness of breath, and nausea. If someone is experiencing these symptoms, it is important to call 911 immediately. While waiting for medical help, make sure the person rests and stays calm. Loosen any tight clothing and help them take an aspirin if they have one.
Stroke:
A stroke occurs when there is a blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain, leading to a lack of oxygen and blood supply to the brain. Symptoms of a stroke include sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body, slurred speech, and difficulty walking. If someone is experiencing these symptoms, call 911 immediately. While waiting for medical help, make sure the person is lying flat on their back with their head slightly elevated. Do not give them any food or drink.
Seizures:
Seizures occur when there is abnormal electrical activity in the brain, leading to involuntary movements and loss of consciousness. If someone is having a seizure, it is important to keep them safe by moving any dangerous objects away from them. Do not try to restrain them or put anything in their mouth. Time the seizure and call 911 if it lasts longer than 5 minutes or if the person is injured.
Allergic Reactions:
Allergic reactions can range from mild to severe and can be life-threatening in some cases. Symptoms include itching, hives, swelling, difficulty breathing, and decreased blood pressure. If someone is experiencing a severe allergic reaction, call 911 immediately. If they have an EpiPen, help them use it. If they have any other medication for their allergy, help them take it as well.
Choking:
Choking occurs when an object becomes lodged in the throat, blocking the airway. If someone is choking, it is important to act quickly. Ask them if they can speak or cough, which means the airway is partially open. If they cannot speak or cough, perform the Heimlich maneuver by standing behind them, wrapping your arms around their waist, and pulling upward and inward on their abdomen.
Burns:
Burns can be caused by heat, chemicals, electricity, or radiation. If someone has a burn, it is important to remove any clothing or jewelry near the burn area and run cool water over the burn for at least 20 minutes. Do not apply ice or butter to the burn. If the burn is severe, cover it with a clean, dry cloth and call 911.
Trauma:
Trauma can range from minor injuries to life-threatening situations. If someone has experienced trauma, it is important to call 911 immediately. While waiting for medical help, keep them calm and make sure they are lying flat on their back. Do not move them unless it is absolutely necessary.
Preparing for Medical Emergencies
Here are some simple steps you can take to prepare for medical emergencies
- Know the location of the nearest hospital.
- Keep a list of medications you are taking.
- Know how to perform CPR.
- Know the emergency services phone numbers.
- Carry an epinephrine auto-injector if prescribed, and avoid known allergens.
- Learn the Heimlich maneuver.
- Keep a first aid kit with burn dressings.
- Know the location of the nearest poison control center, keep all toxic substances out of reach of children.
- Consider Medical Evacuation Insurance.
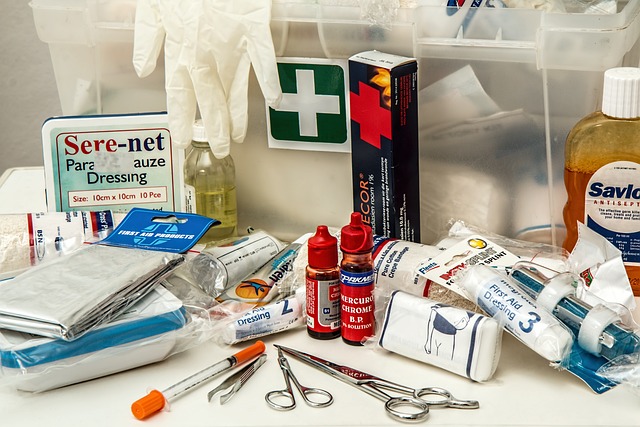
What to Include in a First-Aid Kit
First-Aid kits can be basic for cuts and bee-stings, or they can be extensive and ready to initially treat deep cuts, traumas, heart attacks, etc. Here’s a list of 20 items to consider including in your starter first aid kit:
- Adhesive bandages (assorted sizes)
- Sterile gauze pads
- Medical tape
- Alcohol wipes
- Antiseptic ointment
- Hydrogen peroxide
- Tweezers
- Scissors
- Disposable gloves
- Instant cold packs
- Thermometer
- CPR face shield
- Elastic bandages
- Sterile eyewash solution
- Cotton swabs
- Pain relievers (such as aspirin or ibuprofen)
- Antihistamines (for allergic reactions)
- Emergency blanket
- Quick Clot
- Tourniquet
It’s important to note that the contents of a first aid kit may vary depending on individual needs and activities. It’s always a good idea to periodically check and replenish your first aid kit to ensure that all supplies are up-to-date and in good condition.
In conclusion, medical emergencies can happen at any time and it’s important to be prepared. Knowing how to respond to different types of medical emergencies can help you provide the best possible care. Make sure to know the location of the nearest hospital and emergency services, keep a first aid kit with essential items, and know how to perform basic first aid techniques.
It is our mission to educate, equip, and empower everyday ordinary civilians to understand, prepare for, and survive any emergency they face. We cannot rely on the government to take care of us. We must take it upon ourselves to provide for and protect ourselves and our families.
Note: I am an affiliate with Amazon and may receive a commission from products purchased from Amazon. This helps me continue to put out emergency preparedness information for you.